 The Framework of the Face Hallucination Based on Neighbor Embedding via Illumination Adaptation.
The Framework of the Face Hallucination Based on Neighbor Embedding via Illumination Adaptation.Abstract
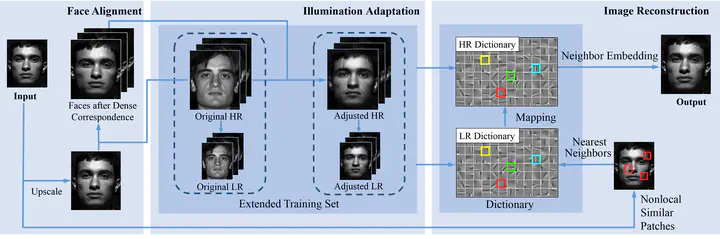
In this paper, we present a novel face hallucination method by neighbor embedding considering illumination adaptation (NEIA) to super-resolve faces when the lighting conditions of the training faces mismatch those of the testing face. For illumination adjustment, face alignment is employed through dense correspondence. Next, every training face is composed into two layers to extract both details and highlight components. By operating the two layers of each face respectively, an extended training set is acquired by combining the original and adapted faces compensated in illumination. Finally, we reconstruct the input faces through neighbor embedding. To improve the estimation of neighbor embedding coefficients, nonlocal similarity is taken into consideration. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms other state-of-the-art methods both in subjective and objective qualities.